Recap
Recap
Last week we talked about
- Classes - the ‘plan’ or ‘blueprint’ for how to make..
- Objects - blocks of memory containing..
- Member Variables - stored within the class and..
- References - ‘pointers’ to objects so we can find and use them
A Simple Class
class Foo {
int x;
int y;
}
Foo f = new Foo();
f.x = 42;
f.y = 9;
System.out.println(f.x);
A number of things happened in one line Foo f = new Foo();
Foo f- create a label (or reference) calledfnew- creates a new objectFoo()- using a plan (or class) called Foof = ..- attach the reference to the object
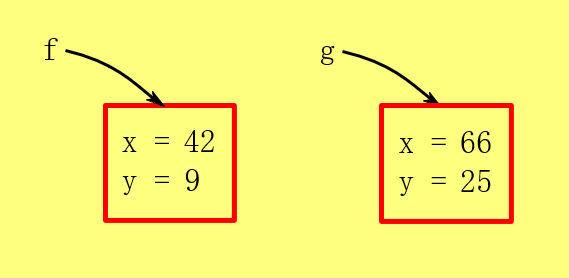
Multiple Objects Of The Same Class
Foo f = new Foo();
f.x = 42;
f.y = 9;
Foo g = new Foo();
g.x = 66;
g.y = 25;
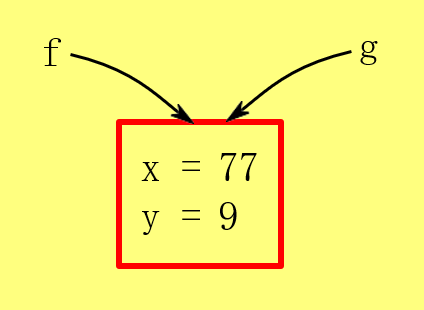
Multiple References To A Single Object
Remember the references and the objects are different things in memory. It is possible to have multiple references all connected to a single object.
Foo f = new Foo();
f.x = 42;
f.y = 9;
Foo g = f;
g.x = 77;